 Spring 快速开始
Spring 快速开始
包结构, HelloWorld
# Spring 的几个特性
- 非侵入式 : 不用"知道"框架代码(不继承框架类,不实现框架接口),耦合低,代码可迁移。
- 依赖注入 : DI(Dependencies Injection),反转控制(IOC)的经典实现。
- 面向切面编程 (AOP)
- 容器 : Spring 是一个容器,其可以管理应用对象的生命周期。
- 组件化 : 可以用简单的组件组合成复杂的应用,在 Spring 中用 XML 或者注解组合对象。
- 一站式 : 在 IOC 和 AOP 上整合了广泛的三方类库。
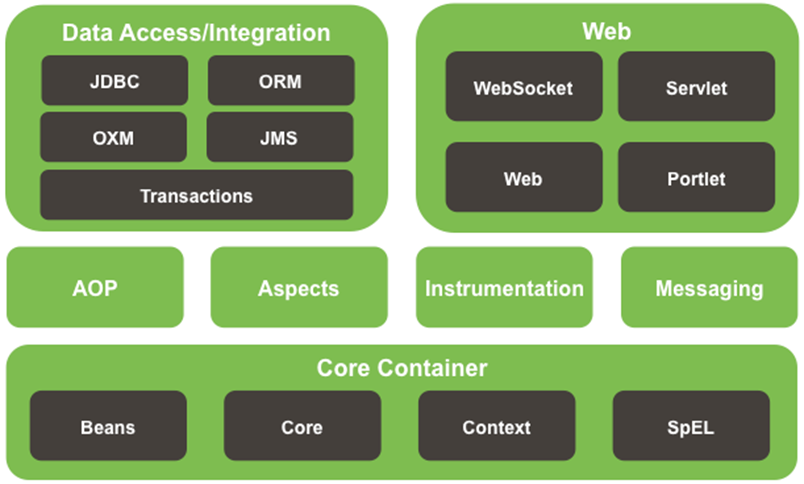
# Spring 模块及 jar 包解释
Spring 下载地址: repo.spring.io (opens new window) Artifact> libs-release-local> org > springframework> spring> Version
# Jar包解释
包名 context 为 spring-context-xxx.RELEASE.jar. 代表 YES; 功能多,按需引入,核心包必须引入。
# Spring 依赖
- commons-logging : Spring所需依赖,需要下载
# 核心容器(Core Container)
- spring-core:核心类库,其他模块大量使用此jar包;
- spring-beans:Spring定义Bean的支持;
- spring-context:运行时Spring容器;
- spring-context-support:Spring容器对第三方包的集成支持,比如邮件服务、视图解析
- spring-expression:Spring表达式语言
# AOP
- spring-aop:基于代理的AOP支持;
- spring-aspects:基于AspectJ的AOP支持;
- spring-instrument:提供一些类级的工具支持和ClassLoader级的实现,用于服务器;
- spring-instrument-tomcat:针对tomcat的instrument实现;
# 数据访问/集成
- spring-jdbc:提供以jdbc访问数据库的支持;
- spring-tx:提供编程式和声明式事务支持;
- spring-orm:提供对象/关系映射支持;
- spring-oxm:提供对象/xml映射支持;
- spring-jms:提供对JMS(java消息服务)的支持;
# web
- spring-web:提供基础的web集成功能;
- spring-webmvc:基于servlet的MVC;
- spring-webmvc-portlet:基于portlet的mvc实现;
- spring-websocket:提供websocket功能;
# test&messaging
- spring-test:spring测试,提供junit与mock测试功能;
- spring-messaging:对消息架构和协议的支持;
# HelloWorld
Spring HellWorld in Intellij IDEA
1.创建普通的 maven 项目
2.导入 Spring 的核心包
Step1: [手动导入]在项目路径下创建 libs 文件夹, 把 core, bean, context, expression和 commons-logging 放入其中。
Step2: 在 Project Structer > Libraries 中添加一个库,选择上面的包,加入到库中。
Step3: 在 Project Structer > Module 中勾选这个库, 让库作用到项目中。
3.创建Bean类
package com.example;
class Student {
public String name;
}
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
4.在 resources中创建 spring 配置文件:
// New File > XML Configration File > Spring Config `创建 spring.xml.
// 注: 先导入 spring-context 包后才有 Spring config 这个选项。
// 直接创建 xml 没有 Spring xml 的命名空间,也就没有标签提示
<beans xxx命名空间xxx>
<bean id="student" class="com.example.Student">
<property name="name" value="randy" />
</bean>
</beans>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
5.主方法中,让容器根据配置文件自动创建对象
main() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
Student student =(Student) context.getBean("student");
System.out.println(student.name);
}
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
6.总结
Spring 可以根据配置文件,帮我们生成对象,且可以帮我们初始化、组装对象,用配置文件批量化 new对象 + 初始化这个对象 + 组装对象的流程。
下一节,了解一个实体对象成员属性为不通的类型,如何通过配置文件为其赋值。
